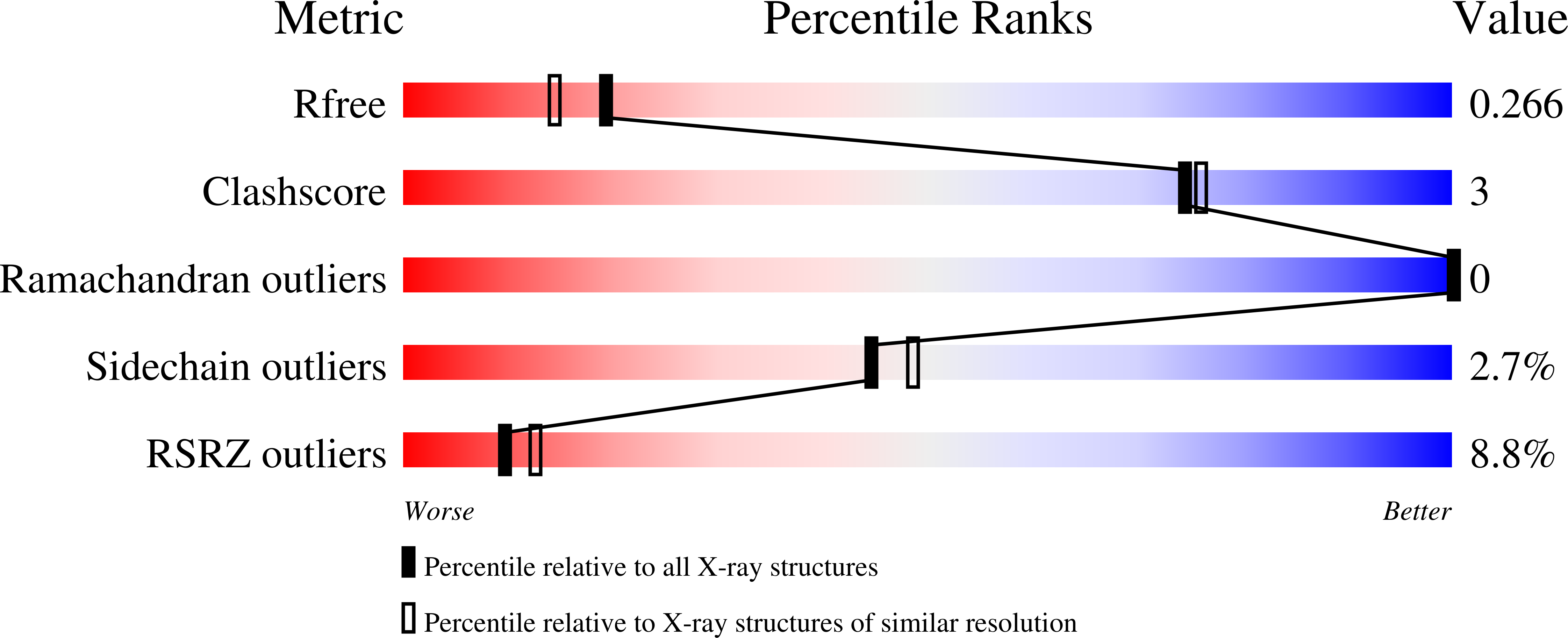
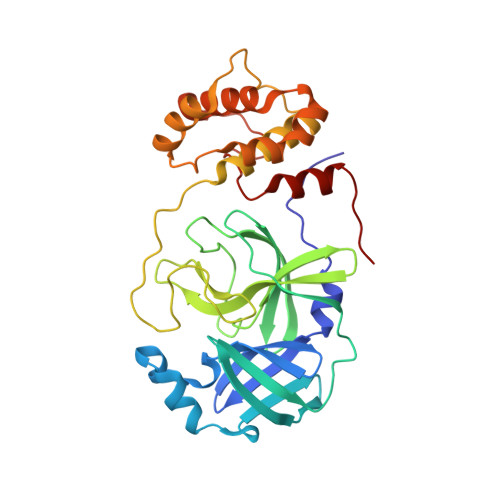
SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibition by a zinc ion: structural features and hints for drug design.
Grifagni, D., Calderone, V., Giuntini, S., Cantini, F., Fragai, M., Banci, L.(2021) Chem Commun (Camb) 57: 7910-7913
- PubMed: 34278402
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cc02956h
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NWX, 7NXH - PubMed Abstract:
Structural data on the SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with a zinc-containing organic inhibitor are already present in the literature and gave hints on the presence of a zinc binding site involving the catalytically relevant cysteine and histidine residues. In this paper, the structural basis of ionic zinc binding to the SARS-CoV-2 main protease has been elucidated by X-ray crystallography. The zinc binding affinity and its ability to inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 main protease have been investigated. These findings provide solid ground for the design of potent and selective metal-conjugated inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Magnetic Resonance Center (CERM), University of Florence, via Sacconi 6, Sesto Fiorentino, 50019, Italy. francesca.cantini@unifi.it marco.fragai@unifi.it lucia.banci@unifi.it.