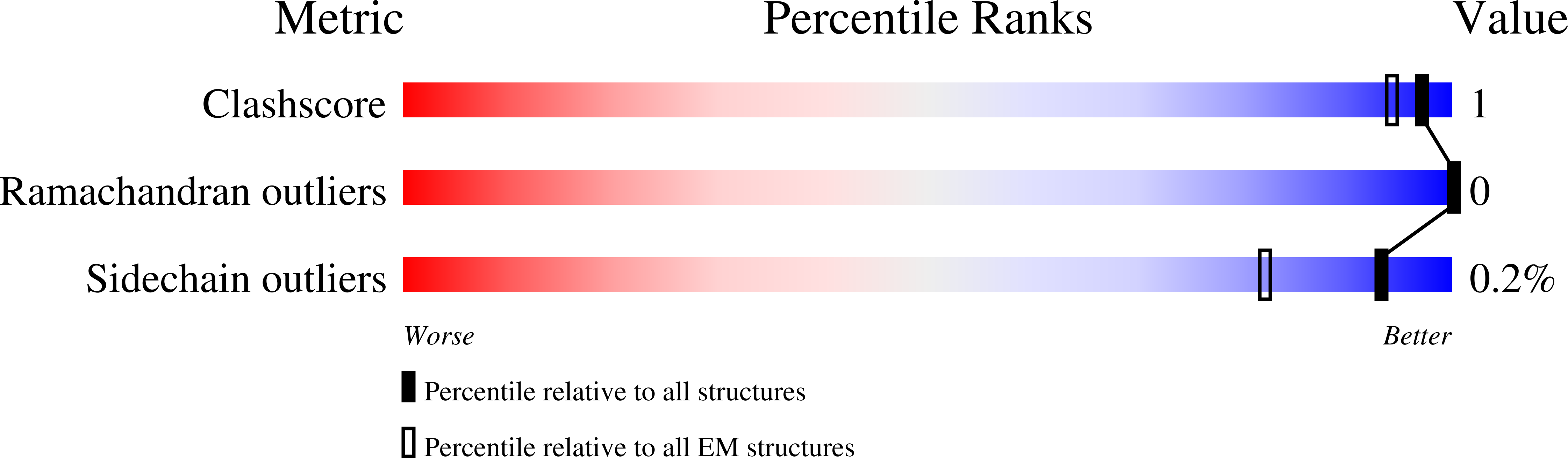Structural insights of a highly potent pan-neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 human monoclonal antibody.
Torres, J.L., Ozorowski, G., Andreano, E., Liu, H., Copps, J., Piccini, G., Donnici, L., Conti, M., Planchais, C., Planas, D., Manganaro, N., Pantano, E., Paciello, I., Pileri, P., Bruel, T., Montomoli, E., Mouquet, H., Schwartz, O., Sala, C., De Francesco, R., Wilson, I.A., Rappuoli, R., Ward, A.B.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2120976119-e2120976119
- PubMed: 35549549
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2120976119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7S6I, 7S6J, 7S6K, 7S6L, 7SBU - PubMed Abstract:
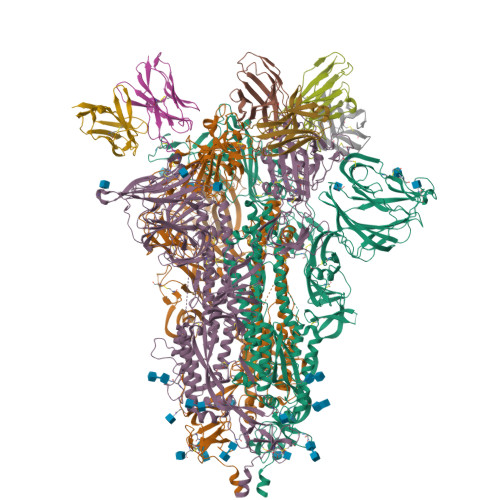
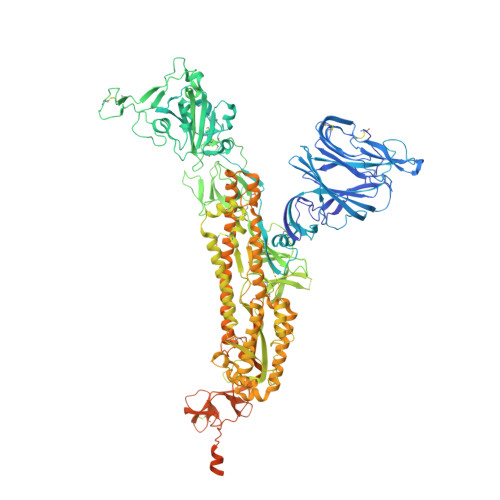
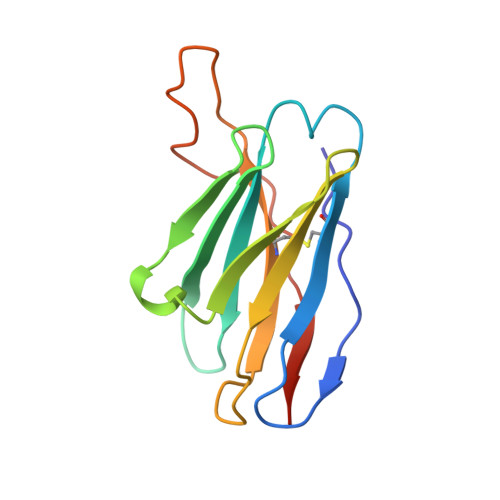
As the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues, there is a strong need for highly potent monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that are resistant against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VoCs). Here, we evaluate the potency of the previously described mAb J08 against these variants using cell-based assays and delve into the molecular details of the binding interaction using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) and X-ray crystallography. We show that mAb J08 has low nanomolar affinity against most VoCs and binds high on the receptor binding domain (RBD) ridge, away from many VoC mutations. These findings further validate the phase II/III human clinical trial underway using mAb J08 as a monoclonal therapy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Integrative Structural and Computational Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92037.