Measles and Nipah virus assembly: Specific lipid binding drives matrix polymerization.
Norris, M.J., Husby, M.L., Kiosses, W.B., Yin, J., Saxena, R., Rennick, L.J., Heiner, A., Harkins, S.S., Pokhrel, R., Schendel, S.L., Hastie, K.M., Landeras-Bueno, S., Salie, Z.L., Lee, B., Chapagain, P.P., Maisner, A., Duprex, W.P., Stahelin, R.V., Saphire, E.O.(2022) Sci Adv 8: eabn1440-eabn1440
- PubMed: 35857835
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abn1440
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
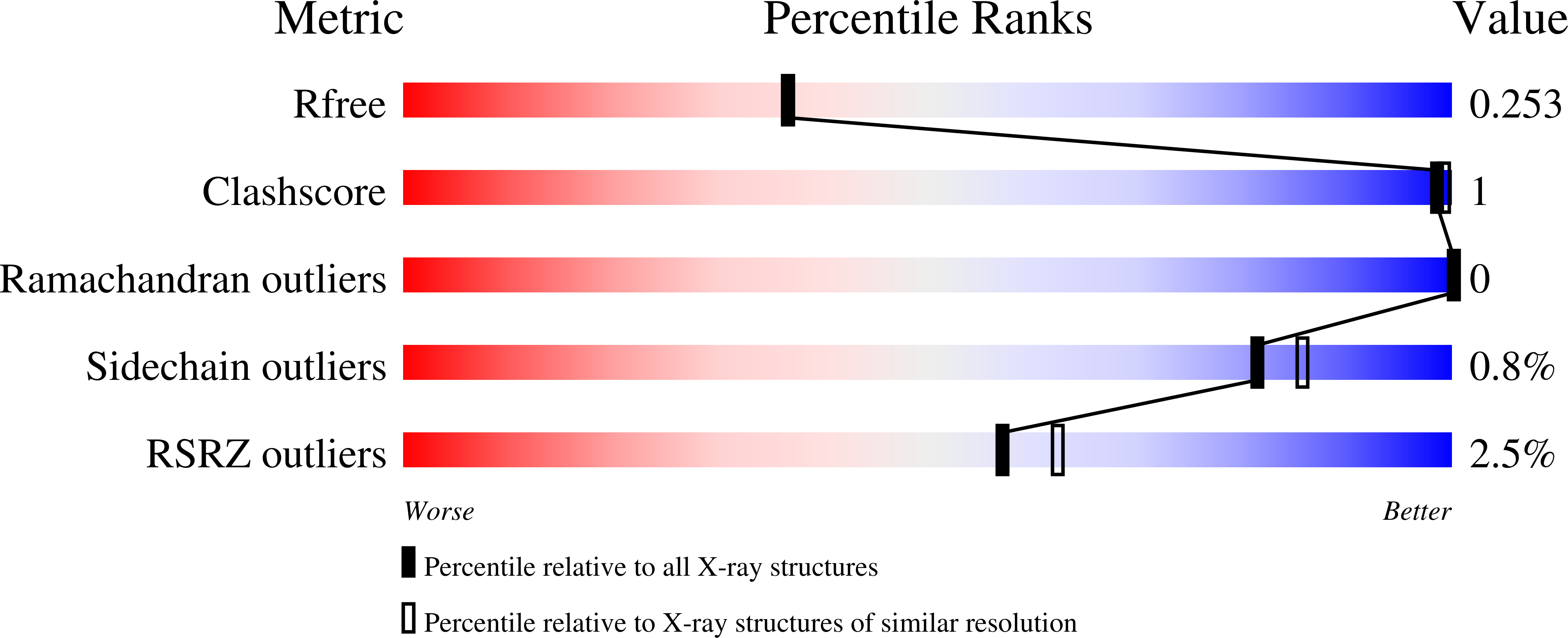
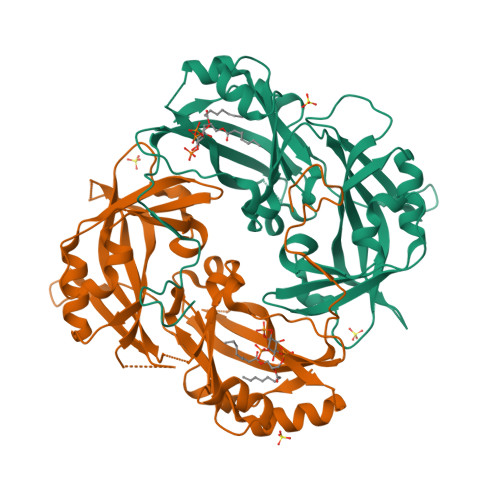
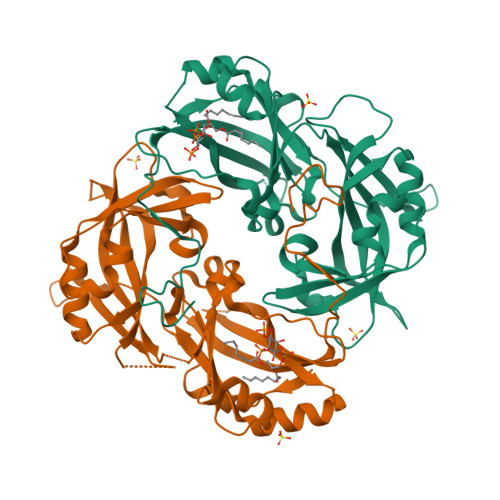
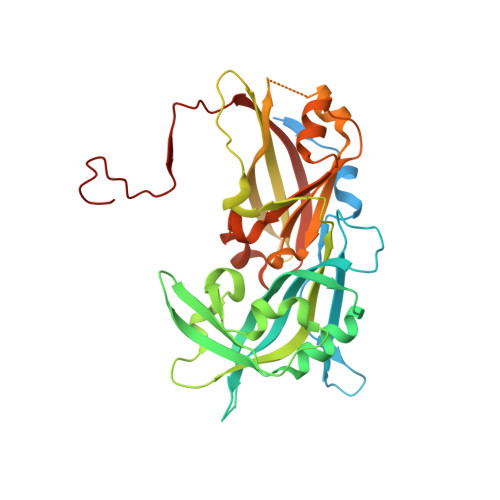
7SKS, 7SKT, 7SKU - PubMed Abstract:
Measles virus, Nipah virus, and multiple other paramyxoviruses cause disease outbreaks in humans and animals worldwide. The paramyxovirus matrix (M) protein mediates virion assembly and budding from host cell membranes. M is thus a key target for antivirals, but few high-resolution structures of paramyxovirus M are available, and we lack the clear understanding of how viral M proteins interact with membrane lipids to mediate viral assembly and egress that is needed to guide antiviral design. Here, we reveal that M proteins associate with phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P 2 ] at the plasma membrane. Using x-ray crystallography, electron microscopy, and molecular dynamics, we demonstrate that PI(4,5)P 2 binding induces conformational and electrostatic changes in the M protein surface that trigger membrane deformation, matrix layer polymerization, and virion assembly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Infectious Disease and Vaccine Research, La Jolla Institute for Immunology, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.