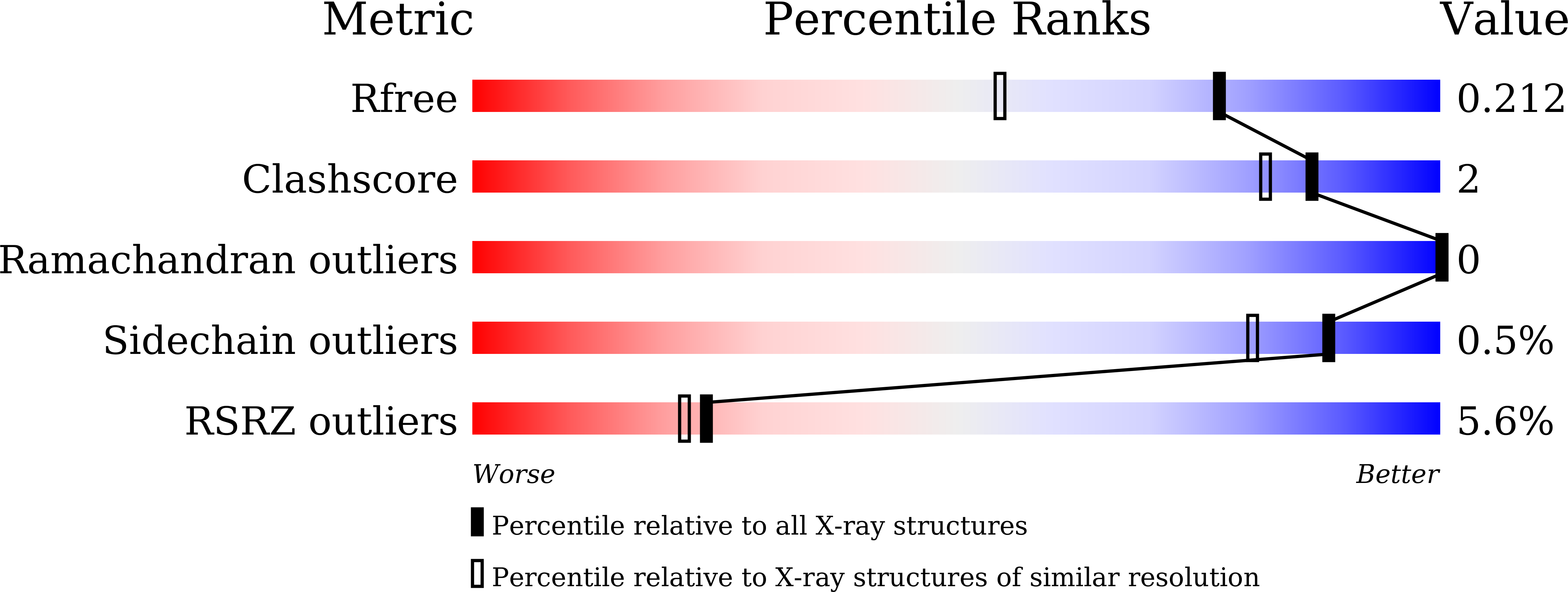
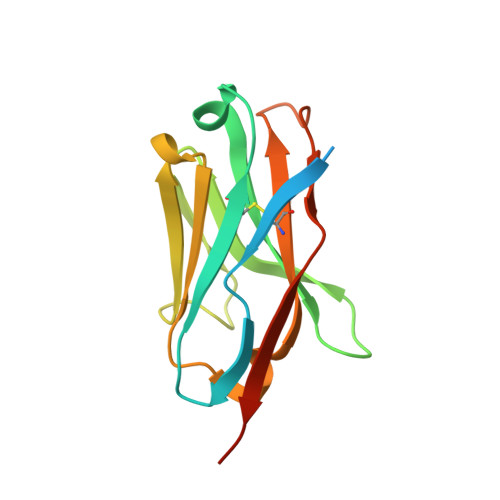
A panel of nanobodies recognizing conserved hidden clefts of all SARS-CoV-2 spike variants including Omicron.
Maeda, R., Fujita, J., Konishi, Y., Kazuma, Y., Yamazaki, H., Anzai, I., Watanabe, T., Yamaguchi, K., Kasai, K., Nagata, K., Yamaoka, Y., Miyakawa, K., Ryo, A., Shirakawa, K., Sato, K., Makino, F., Matsuura, Y., Inoue, T., Imura, A., Namba, K., Takaori-Kondo, A.(2022) Commun Biol 5: 669-669
- PubMed: 35794202
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03630-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VPY, 7VQ0 - PubMed Abstract:
We are amid the historic coronavirus infectious disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Imbalances in the accessibility of vaccines, medicines, and diagnostics among countries, regions, and populations, and those in war crises, have been problematic. Nanobodies are small, stable, customizable, and inexpensive to produce. Herein, we present a panel of nanobodies that can detect the spike proteins of five SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) including Omicron. Here we show via ELISA, lateral flow, kinetic, flow cytometric, microscopy, and Western blotting assays that our nanobodies can quantify the spike variants. This panel of nanobodies broadly neutralizes viral infection caused by pseudotyped and authentic SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. Structural analyses show that the P86 clone targets epitopes that are conserved yet unclassified on the receptor-binding domain (RBD) and contacts the N-terminal domain (NTD). Human antibodies rarely access both regions; consequently, the clone buries hidden crevasses of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins that go undetected by conventional antibodies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Haematology and Oncology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, 606-8507, Japan. maeda@cognano.co.jp.