A Potent Neutralizing Nanobody Targeting the Spike Receptor-Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and the Structural Basis of Its Intimate Binding.
Yang, J., Lin, S., Sun, H., Chen, Z., Yang, F., Lin, X., Guo, L., Wang, L., Wen, A., Zhang, X., Dai, Y., He, B., Cao, Y., Dong, H., Liu, X., Chen, B., Li, J., Zhao, Q., Lu, G.(2022) Front Immunol 13: 820336-820336
- PubMed: 35663966
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.820336
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
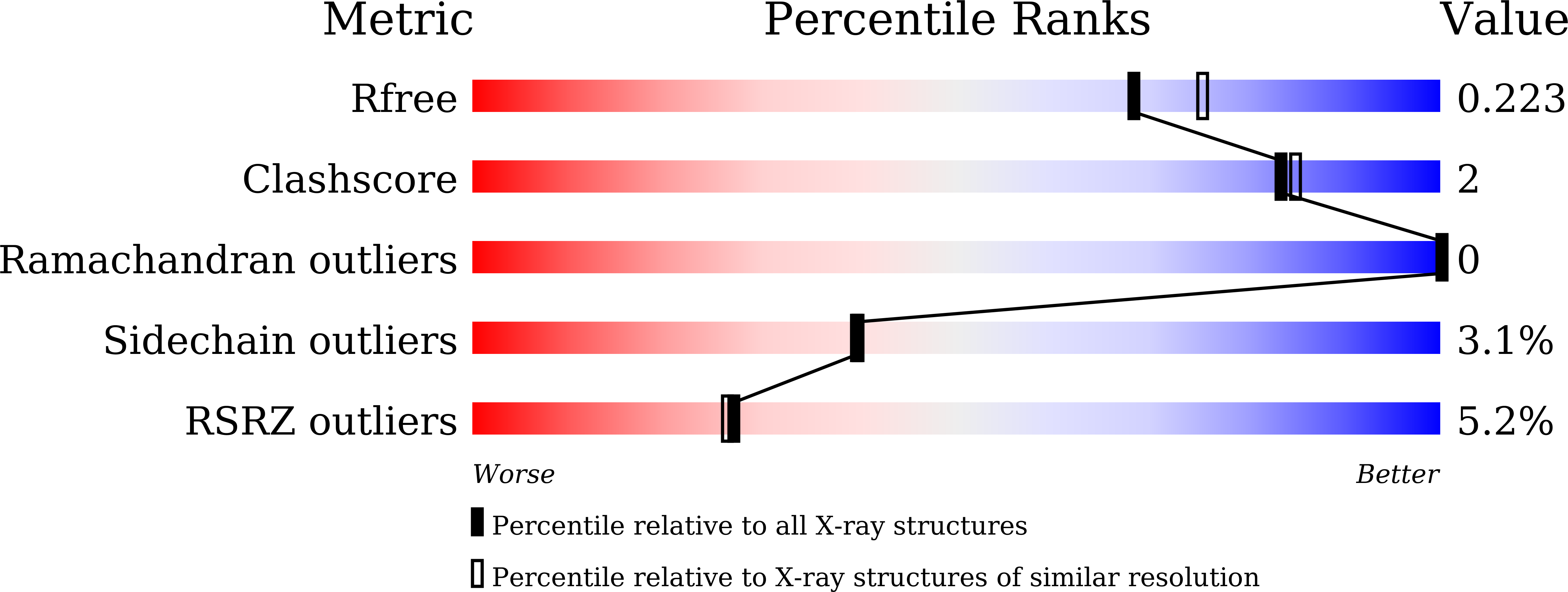
7W1S - PubMed Abstract:
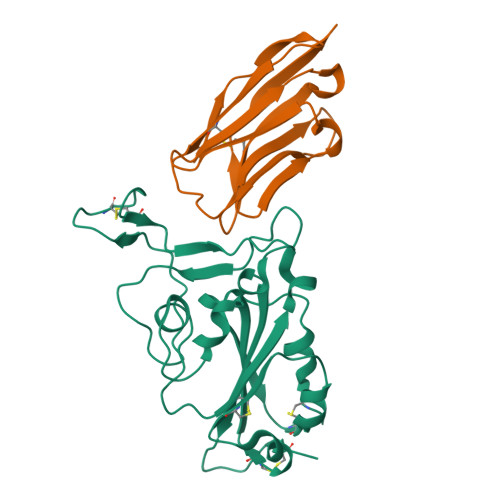
The continuous spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) around the world has raised unprecedented challenges to the human society. Antibodies and nanobodies possessing neutralization activity represent promising drug candidates. In this study, we report the identification and characterization of a potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing nanobody that targets the viral spike receptor-binding domain (S-RBD). The nanobody, termed as Nb-007, engages SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD with the two-digit picomolar binding affinity and shows outstanding virus entry-inhibition activity. The complex structure of Nb-007 bound to SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD reveals an epitope that is partially overlapping with the binding site for the human receptor of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). The nanobody therefore exerts neutralization by competing with ACE2 for S-RBD binding, which is further ascertained by our in-vitro biochemical analyses. Finally, we also show that Nb-007 reserves promising, though compromised, neutralization activity against the currently-circulating Delta variant and that fusion of the nanobody with Fc dramatically increases its entry-inhibition capacity. Taken together, these data have paved the way of developing Nb-007 as a drug-reserve for potential treatment of SARS-CoV-2 related diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
West China Hospital Emergency Department (WCHED), State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.