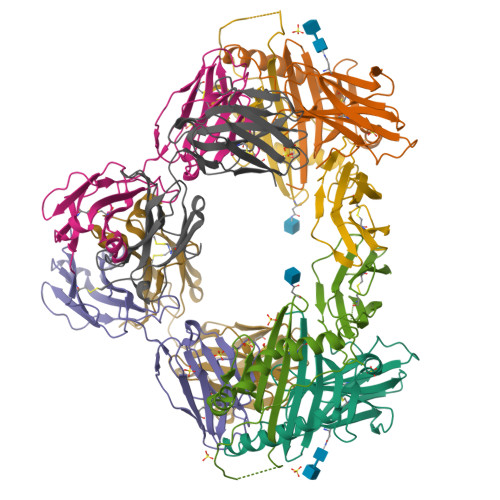
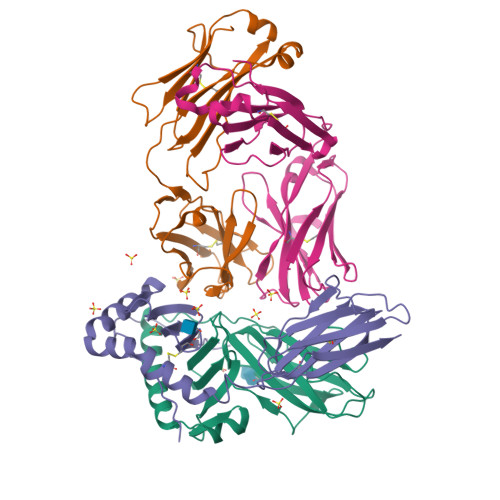
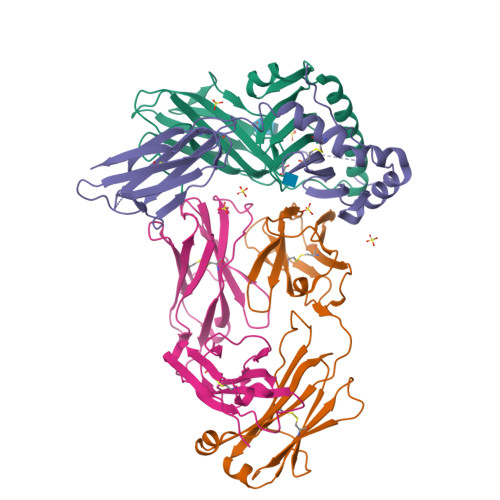
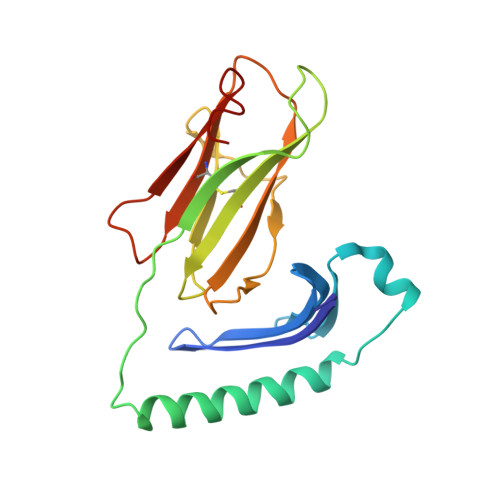
Modular adjuvant-free pan-HLA-DR-immunotargeting subunit vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 elicits broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody responses.
Kassardjian, A., Sun, E., Sookhoo, J., Muthuraman, K., Boligan, K.F., Kucharska, I., Rujas, E., Jetha, A., Branch, D.R., Babiuk, S., Barber, B., Julien, J.P.(2023) Cell Rep 42: 112391-112391
- PubMed: 37053069
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112391
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EUQ - PubMed Abstract:
Subunit vaccines typically require co-administration with an adjuvant to elicit protective immunity, adding development hurdles that can impede rapid pandemic responses. To circumvent the need for adjuvant in a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) subunit vaccine, we engineer a thermostable immunotargeting vaccine (ITV) that leverages the pan-HLA-DR monoclonal antibody 44H10 to deliver the viral spike protein receptor-binding domain (RBD) to antigen-presenting cells. X-ray crystallography shows that 44H10 binds to a conserved epitope on HLA-DR, providing the basis for its broad HLA-DR reactivity. Adjuvant-free ITV immunization in rabbits and ferrets induces robust anti-RBD antibody responses that neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and protect recipients from SARS-CoV-2 challenge. We demonstrate that the modular nature of the ITV scaffold with respect to helper T cell epitopes and diverse RBD antigens facilitates broad sarbecovirus neutralization. Our findings support anti-HLA-DR immunotargeting as an effective means to induce strong antibody responses to subunit antigens without requiring an adjuvant.
Organizational Affiliation:
Program in Molecular Medicine, The Hospital for Sick Children Research Institute, Toronto, ON M5G 0A4, Canada; Department of Immunology, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON M5S 1A8, Canada.