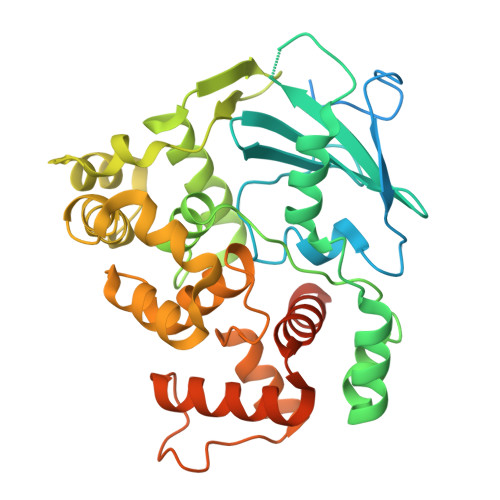
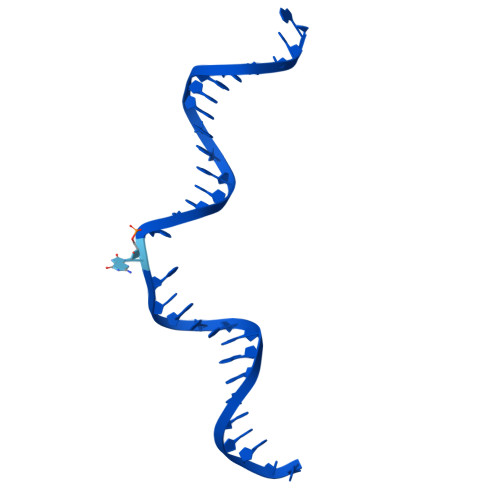
Human 8-oxoguanine glycosylase OGG1 binds nucleosome at the dsDNA ends and the super-helical locations.
You, Q., Feng, X., Cai, Y., Baylin, S.B., Li, H.(2024) Commun Biol 7: 1202-1202
- PubMed: 39341999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-06919-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8VX4, 8VX5, 8VX6 - PubMed Abstract:
The human glycosylase OGG1 extrudes and excises the oxidized DNA base 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) to initiate base excision repair and plays important roles in many pathological conditions such as cancer, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases. Previous structural studies have used a truncated protein and short linear DNA, so it has been unclear how full-length OGG1 operates on longer DNA or on nucleosomes. Here we report cryo-EM structures of human OGG1 bound to a 35-bp long DNA containing an 8-oxoG within an unmethylated Cp-8-oxoG dinucleotide as well as to a nucleosome with an 8-oxoG at super-helical location (SHL)-5. The 8-oxoG in the linear DNA is flipped out by OGG1, consistent with previous crystallographic findings with a 15-bp DNA. OGG1 preferentially binds near dsDNA ends at the nucleosomal entry/exit sites. Such preference may underlie the enzyme's function in DNA double-strand break repair. Unexpectedly, we find that OGG1 bends the nucleosomal entry DNA, flips an undamaged guanine, and binds to internal nucleosomal DNA sites such as SHL-5 and SHL+6. We suggest that the DNA base search mechanism by OGG1 may be chromatin context-dependent and that OGG1 may partner with chromatin remodelers to excise 8-oxoG at the nucleosomal internal sites.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Van Andel Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, USA.