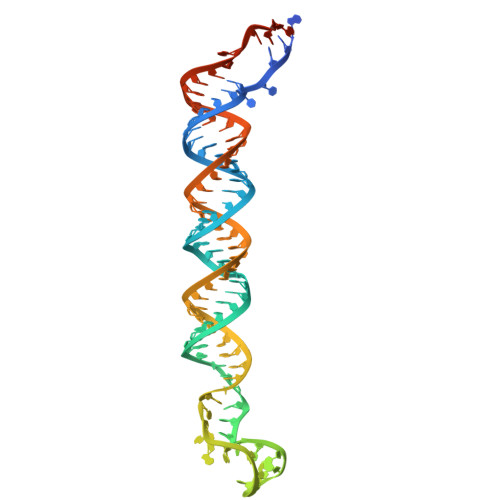
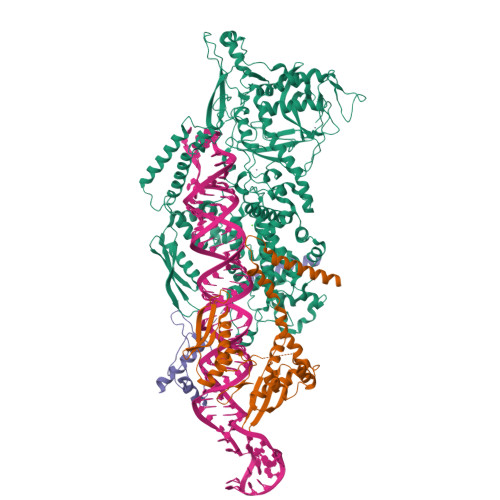
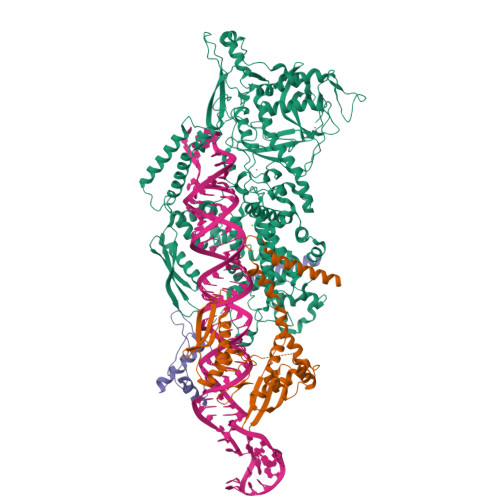
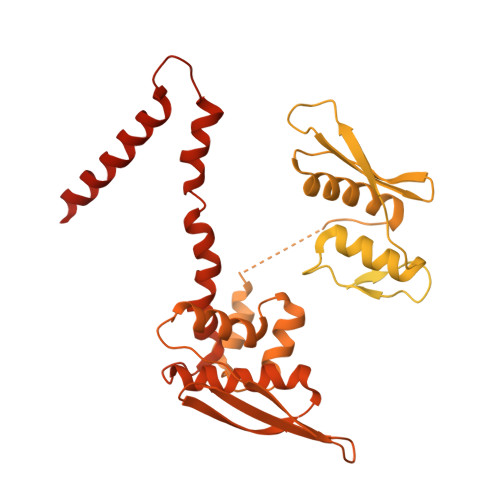
The structural landscape of Microprocessor-mediated processing of pri-let-7 miRNAs.
Garg, A., Shang, R., Cvetanovic, T., Lai, E.C., Joshua-Tor, L.(2024) Mol Cell 84: 4175-4190.e6
- PubMed: 39368465
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2024.09.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9ASM, 9ASN, 9ASO, 9ASP, 9ASQ - PubMed Abstract:
MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis is initiated upon cleavage of a primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) hairpin by the Microprocessor (MP), composed of the Drosha RNase III enzyme and its partner DGCR8. Multiple pri-miRNA sequence motifs affect MP recognition, fidelity, and efficiency. Here, we performed cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) and biochemical studies of several let-7 family pri-miRNAs in complex with human MP. We show that MP has the structural plasticity to accommodate a range of pri-miRNAs. These structures revealed key features of the 5' UG sequence motif, more comprehensively represented as the "flipped U with paired N" (fUN) motif. Our analysis explains how cleavage of class-II pri-let-7 members harboring a bulged nucleotide generates a non-canonical precursor with a 1-nt 3' overhang. Finally, the MP-SRSF3-pri-let-7f1 structure reveals how SRSF3 contributes to MP fidelity by interacting with the CNNC motif and Drosha's Piwi/Argonaute/Zwille (PAZ)-like domain. Overall, this study sheds light on the mechanisms for flexible recognition, accurate cleavage, and regulated processing of different pri-miRNAs by MP.
Organizational Affiliation:
W. M. Keck Structural Biology Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, One Bungtown Road, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724, USA; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, One Bungtown Road, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724, USA.