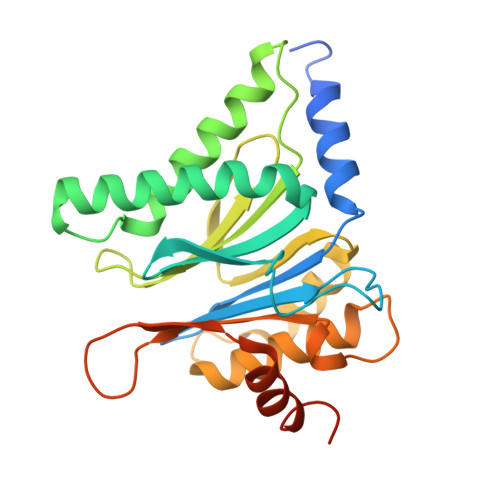
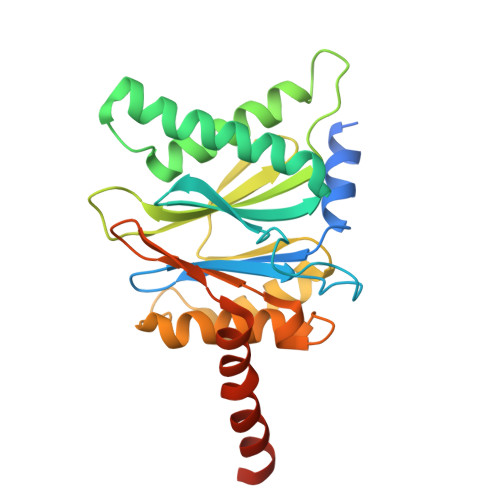
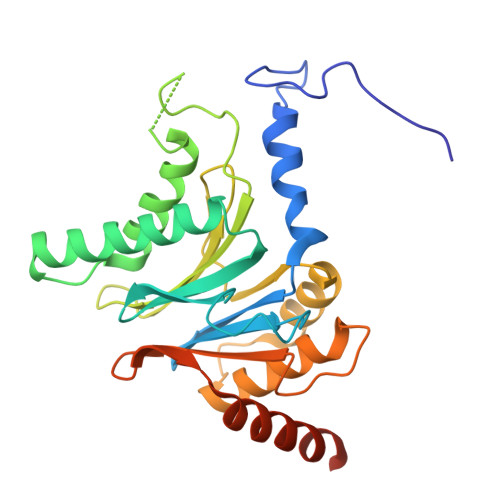
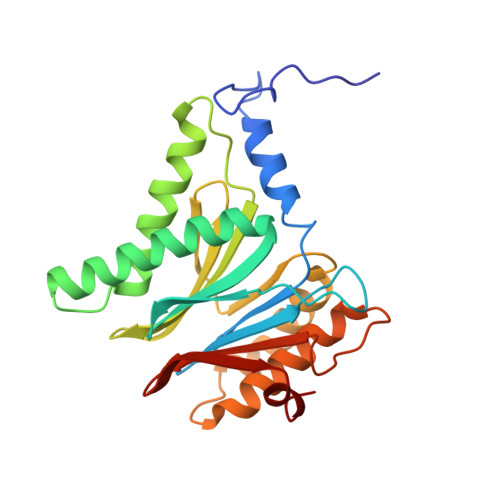
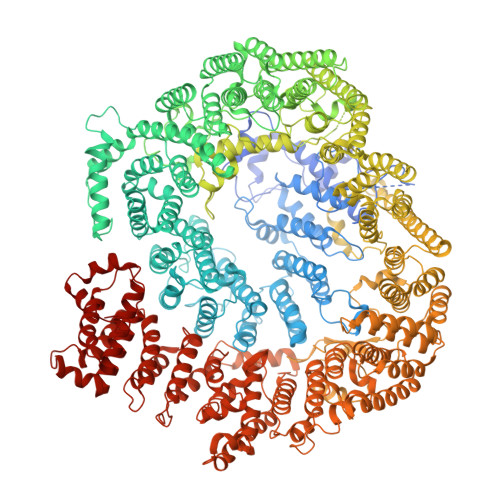
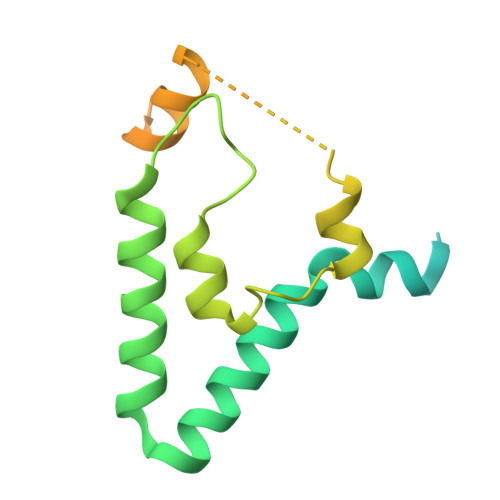
Structure of Blm10:13S proteasome intermediate reveals parallel assembly pathways for the proteasome core particle.
Kaur, M., Chen, X., Lee, S.Y., Weaver, T.M., Freudenthal, B.D., Walters, K.J., Roelofs, J.(2024) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 39574619
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.11.04.621988
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9D0T - PubMed Abstract:
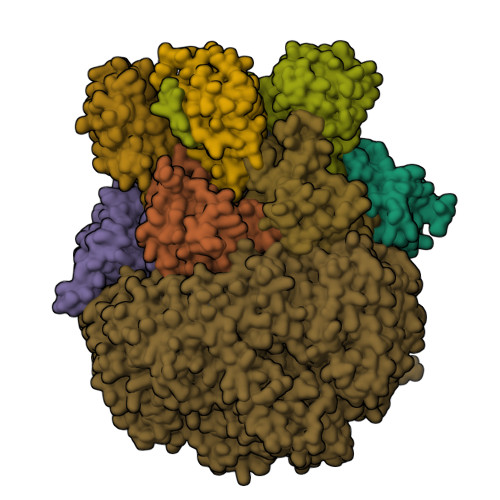
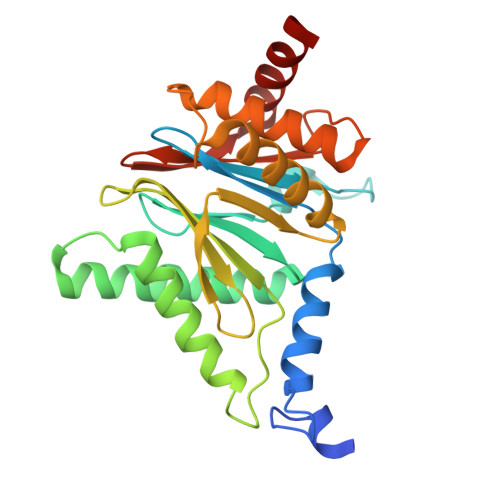
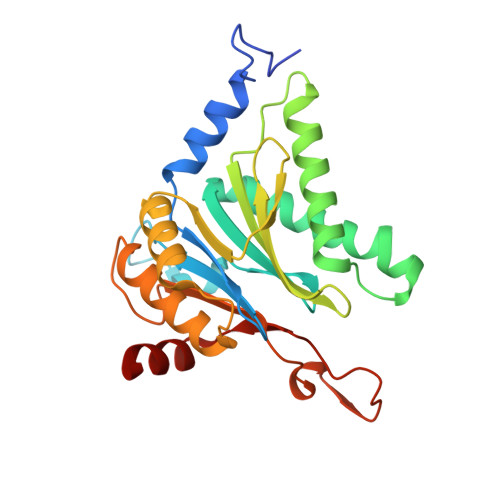
Proteasomes are formed by chaperone-assisted assembly of core particles (CPs) and regulatory particles (RPs). The CP chaperone dimer Pba1/Pba2 binds early to proteasome subunits, and is thought to be replaced by Blm10 to form Blm10:CP, which promotes ATP-independent degradation of disordered proteins. Here, we present evidence of distinct parallel assembly pathways for CP by solving five cryo-EM structures including a Blm10:13S pre-assembly intermediate. Our data conflict with the current model of Blm10 and Pba1/Pba2 sequential activity in a single assembly pathway, as we find their CP binding is mutually exclusive and both are present on early and late assembly intermediates. CP affinity for Pba1/Pba2 is reduced during maturation, promoting Pba1/Pba2 release. We find Blm10 undergoes no such affinity switch, suggesting this pathway predominantly yields mature Blm10-bound CP. Altogether, our findings conflict with the current paradigm of sequential CP binding to instead indicate parallel assembly pathways by Pba1/Pba2 and Blm10.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, 3901 Rainbow Blvd., HLSIC 1077, Kansas, USA.