Probing Ferryl Reactivity in a Nonheme Iron Oxygenase Using an Expanded Genetic Code.
Hardy, F.J., Quesne, M.G., Gerard, E.F., Zhao, J., Ortmayer, M., Taylor, C.J., Ali, H.S., Slater, J.W., Levy, C.W., Heyes, D.J., Bollinger Jr., J.M., de Visser, S.P., Green, A.P.(2024) ACS Catal 14: 11584-11590
- PubMed: 39114090
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.4c02365
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9EQF - PubMed Abstract:
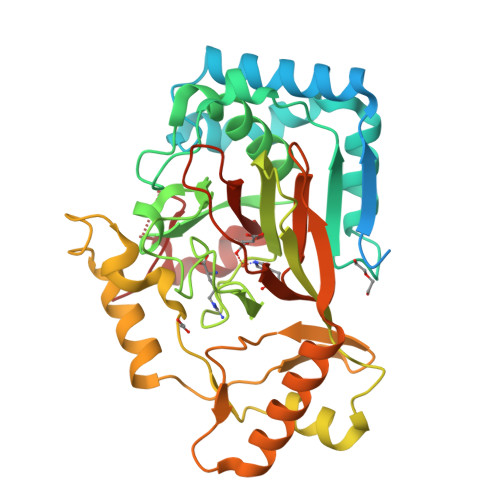
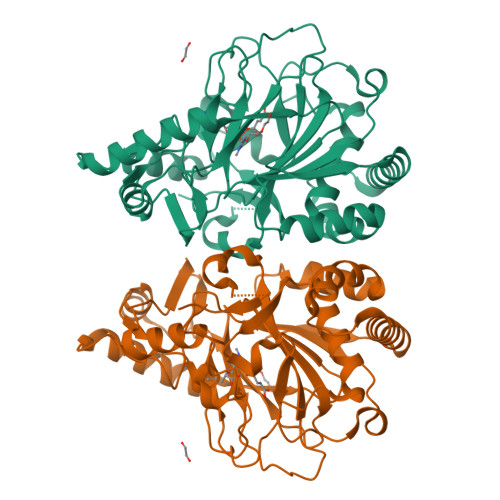
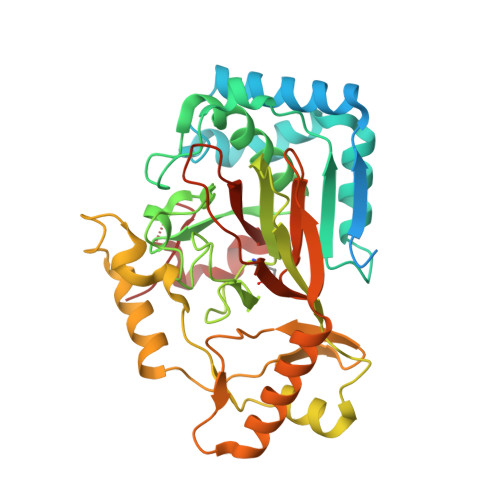
The ability to introduce noncanonical amino acids as axial ligands in heme enzymes has provided a powerful experimental tool for studying the structure and reactivity of their Fe IV =O ("ferryl") intermediates. Here, we show that a similar approach can be used to perturb the conserved Fe coordination environment of 2-oxoglutarate (2OG) dependent oxygenases, a versatile class of enzymes that employ highly-reactive ferryl intermediates to mediate challenging C-H functionalizations. Replacement of one of the cis-disposed histidine ligands in the oxygenase VioC with a less electron donating N δ -methyl-histidine (MeHis) preserves both catalytic function and reaction selectivity. Significantly, the key ferryl intermediate responsible for C-H activation can be accumulated in both the wildtype and the modified protein. In contrast to heme enzymes, where metal-oxo reactivity is extremely sensitive to the nature of the proximal ligand, the rates of C-H activation and the observed large kinetic isotope effects are only minimally affected by axial ligand replacement in VioC. This study showcases a powerful tool for modulating the coordination sphere of nonheme iron enzymes that will enhance our understanding of the factors governing their divergent activities.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry & Manchester Institute of Biotechnology, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess Street, Manchester M1 7DN, U.K.