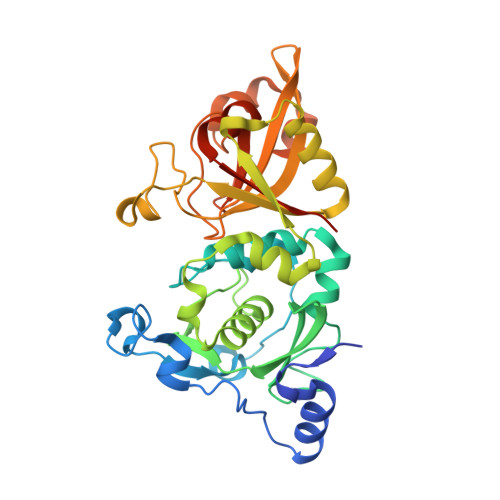
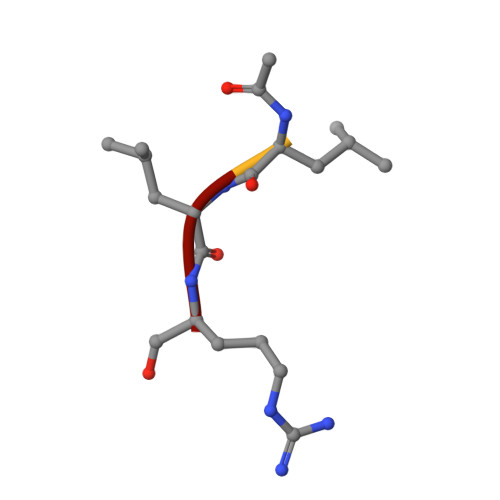
Crystal Structures of Calpain-E64 and -Leupeptin Inhibitor Complexes Reveal Mobile Loops Gating the Active Site
Moldoveanu, T., Campbell, R.L., Cuerrier, D., Davies, P.L.(2004) J Mol Biol 343: 1313-1326
- PubMed: 15491615
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TL9, 1TLO - PubMed Abstract:
The endogenous calpain inhibitor, calpastatin, modulates some patho-physiological aspects of calpain signaling. Excess calpain can escape this inhibition and as well, many calpain isoforms and autolytically generated protease core fragments are not inhibited by calpastatin. There is a need, therefore, to develop specific, cell-permeable calpain inhibitors to block uncontrolled proteolysis and prevent tissue damage during brain and heart ischemia, spinal-cord injury and Alzheimer's diseases. Here, we report the first high-resolution crystal structures of rat mu-calpain protease core complexed with two traditional, low molecular mass inhibitors, leupeptin and E64. These structures show that access to a slightly deeper, but otherwise papain-like active site is gated by two flexible loops. These loops are divergent among the calpain isoforms giving a potential structural basis for substrate/inhibitor selectivity over other papain-like cysteine proteases and between members of the calpain family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Queen's University, Kingston, Ont. K7L 3N6, Canada.