YbxF and YlxQ are bacterial homologs of L7Ae and bind K-turns but not K-loops.
Baird, N.J., Zhang, J., Hamma, T., Ferre-D'Amare, A.R.(2012) RNA 18: 759-770
- PubMed: 22355167
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.031518.111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
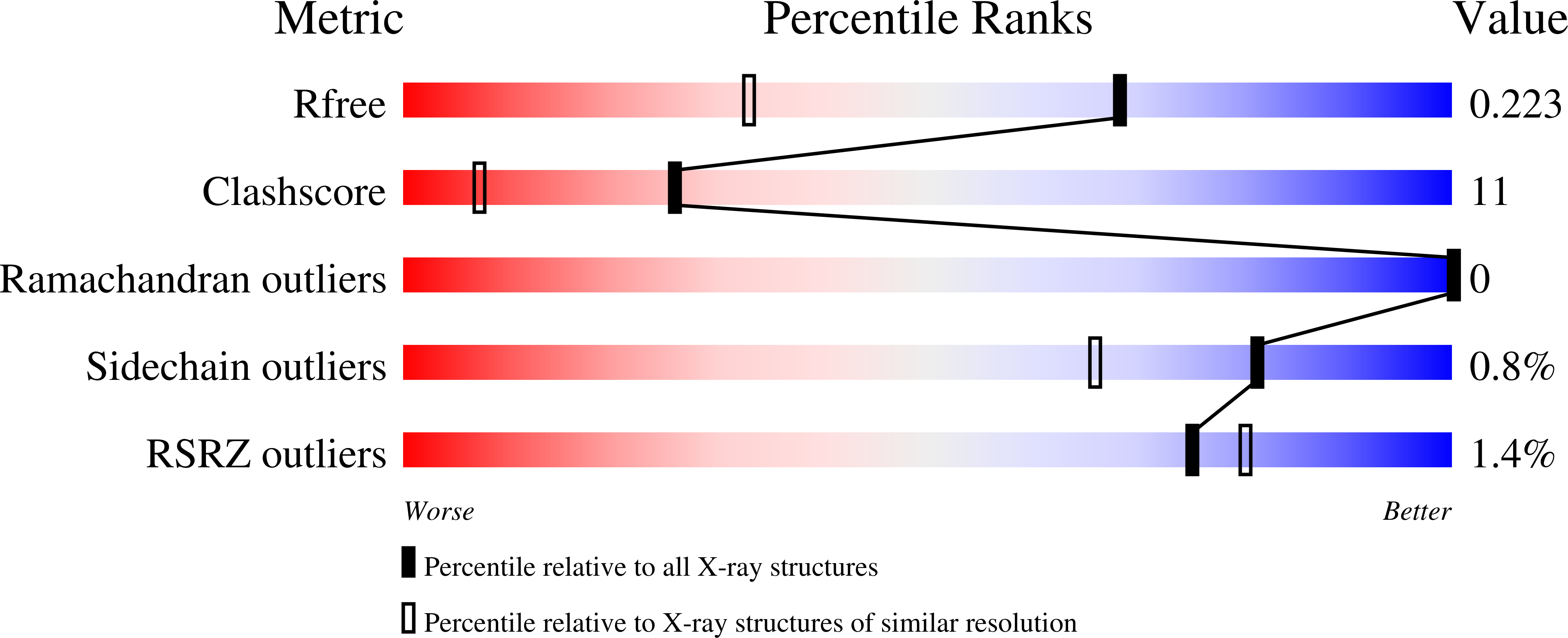
3V7E, 3V7Q - PubMed Abstract:
The archaeal protein L7Ae and eukaryotic homologs such as L30e and 15.5kD comprise the best characterized family of K-turn-binding proteins. K-turns are an RNA motif comprised of a bulge flanked by canonical and noncanonical helices. They are widespread in cellular RNAs, including bacterial gene-regulatory RNAs such as the c-di-GMP-II, lysine, and SAM-I riboswitches, and the T-box. The existence in bacteria of K-turn-binding proteins of the L7Ae family has not been proven, although two hypothetical proteins, YbxF and YlxQ, have been proposed to be L7Ae homologs based on sequence conservation. Using purified, recombinant proteins, we show that Bacillus subtilis YbxF and YlxQ bind K-turns (K(d) ~270 nM and ~2300 nM, respectively). Crystallographic structure determination demonstrates that both YbxF and YlxQ adopt the same overall fold as L7Ae. Unlike the latter, neither bacterial protein recognizes K-loops, a structural motif that lacks the canonical helix of the K-turn. This property is shared between the bacterial and eukaryal family members. Comparison of our structure of YbxF in complex with the K-turn of the SAM-I riboswitch and previously determined structures of archaeal and eukaryal homologs bound to RNA indicates that L7Ae approaches the K-turn at a unique angle, which results in a considerably larger RNA-protein interface dominated by interactions with the noncanonical helix of the K-turn. Thus, the inability of the bacterial and eukaryal L7Ae homologs to bind K-loops probably results from their reliance on interactions with the canonical helix. The biological functions of YbxF and YlxQ remain to be determined.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of RNA Biophysics and Cellular Physiology, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, Bethesda, Maryland 20892-8012, USA.