The Reaction Mechanism of N-Acetylneuraminic Acid Lyase Revealed by a Combination of Crystallography, Qm/Mm Simulation and Mutagenesis.
Daniels, A.D., Campeotto, I., Van Der Kamp, M.W., Bolt, A.H., Trinh, C.H., Phillips, S.E.V., Pearson, A.R., Nelson, A., Mulholland, A.J., Berry, A.(2014) ACS Chem Biol 9: 1025
- PubMed: 24521460
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cb500067z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BWL - PubMed Abstract:
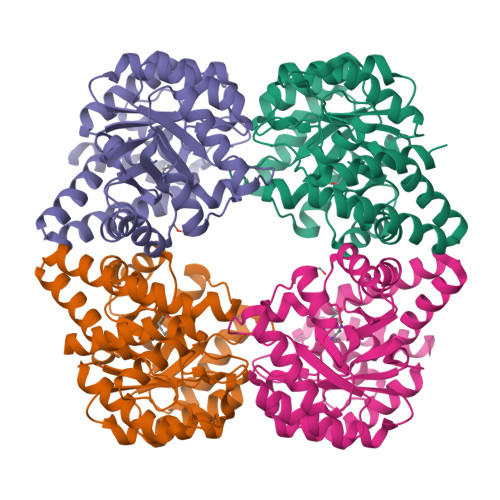
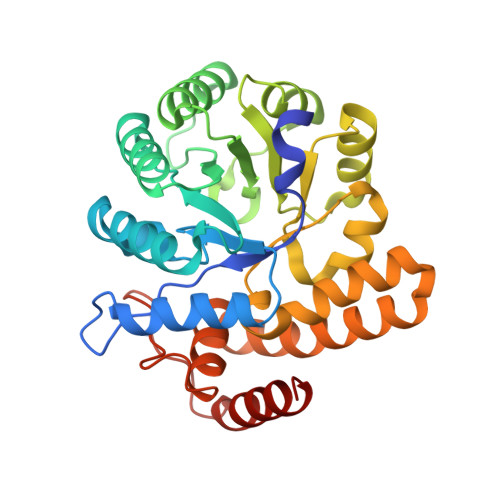
N-Acetylneuraminic acid lyase (NAL) is a Class I aldolase that catalyzes the reversible condensation of pyruvate with N-acetyl-d-mannosamine (ManNAc) to yield the sialic acid N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac). Aldolases are finding increasing use as biocatalysts for the stereospecific synthesis of complex molecules. Incomplete understanding of the mechanism of catalysis in aldolases, however, can hamper development of new enzyme activities and specificities, including control over newly generated stereocenters. In the case of NAL, it is clear that the enzyme catalyzes a Bi-Uni ordered condensation reaction in which pyruvate binds first to the enzyme to form a catalytically important Schiff base. The identity of the residues required for catalysis of the condensation step and the nature of the transition state for this reaction, however, have been a matter of conjecture. In order to address, this we crystallized a Y137A variant of the E. coli NAL in the presence of Neu5Ac. The three-dimensional structure shows a full length sialic acid bound in the active site of subunits A, B, and D, while in subunit C, discontinuous electron density reveals the positions of enzyme-bound pyruvate and ManNAc. These 'snapshot' structures, representative of intermediates in the enzyme catalytic cycle, provided an ideal starting point for QM/MM modeling of the enzymic reaction of carbon-carbon bond formation. This revealed that Tyr137 acts as the proton donor to the aldehyde oxygen of ManNAc during the reaction, the activation barrier is dominated by carbon-carbon bond formation, and proton transfer from Tyr137 is required to obtain a stable Neu5Ac-Lys165 Schiff base complex. The results also suggested that a triad of residues, Tyr137, Ser47, and Tyr110 from a neighboring subunit, are required to correctly position Tyr137 for its function, and this was confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis. This understanding of the mechanism and geometry of the transition states along the C-C bond-forming pathway will allow further development of these enzymes for stereospecific synthesis of new enzyme products.
Organizational Affiliation:
Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology and School of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of Leeds , Leeds LS2 9JT, U.K.