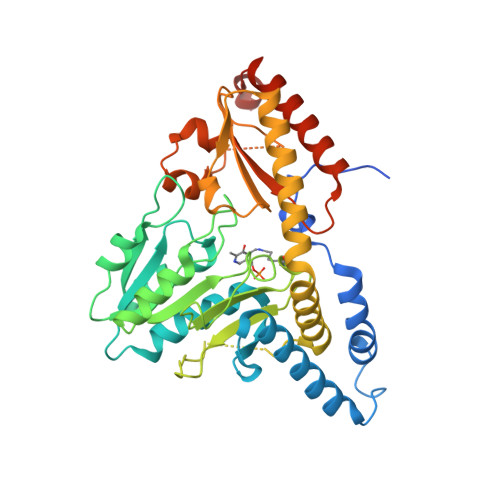
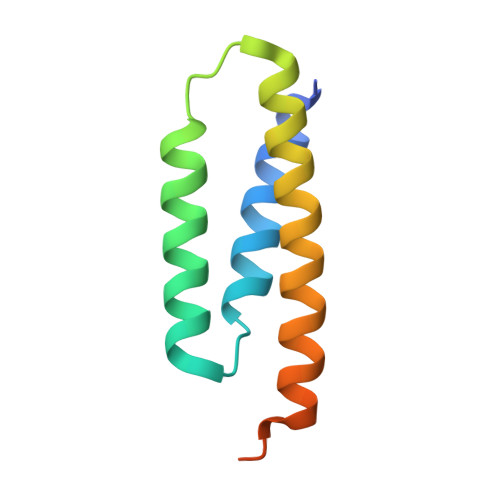
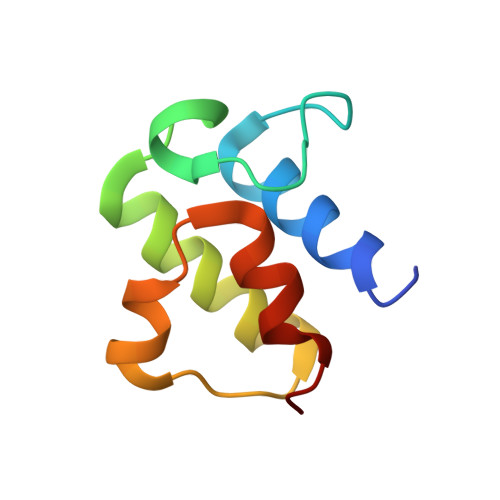
Structure of human Fe-S assembly subcomplex reveals unexpected cysteine desulfurase architecture and acyl-ACP-ISD11 interactions.
Cory, S.A., Van Vranken, J.G., Brignole, E.J., Patra, S., Winge, D.R., Drennan, C.L., Rutter, J., Barondeau, D.P.(2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114: E5325-E5334
- PubMed: 28634302
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702849114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5USR - PubMed Abstract:
In eukaryotes, sulfur is mobilized for incorporation into multiple biosynthetic pathways by a cysteine desulfurase complex that consists of a catalytic subunit (NFS1), LYR protein (ISD11), and acyl carrier protein (ACP). This NFS1-ISD11-ACP (SDA) complex forms the core of the iron-sulfur (Fe-S) assembly complex and associates with assembly proteins ISCU2, frataxin (FXN), and ferredoxin to synthesize Fe-S clusters. Here we present crystallographic and electron microscopic structures of the SDA complex coupled to enzyme kinetic and cell-based studies to provide structure-function properties of a mitochondrial cysteine desulfurase. Unlike prokaryotic cysteine desulfurases, the SDA structure adopts an unexpected architecture in which a pair of ISD11 subunits form the dimeric core of the SDA complex, which clarifies the critical role of ISD11 in eukaryotic assemblies. The different quaternary structure results in an incompletely formed substrate channel and solvent-exposed pyridoxal 5'-phosphate cofactor and provides a rationale for the allosteric activator function of FXN in eukaryotic systems. The structure also reveals the 4'-phosphopantetheine-conjugated acyl-group of ACP occupies the hydrophobic core of ISD11, explaining the basis of ACP stabilization. The unexpected architecture for the SDA complex provides a framework for understanding interactions with acceptor proteins for sulfur-containing biosynthetic pathways, elucidating mechanistic details of eukaryotic Fe-S cluster biosynthesis, and clarifying how defects in Fe-S cluster assembly lead to diseases such as Friedreich's ataxia. Moreover, our results support a lock-and-key model in which LYR proteins associate with acyl-ACP as a mechanism for fatty acid biosynthesis to coordinate the expression, Fe-S cofactor maturation, and activity of the respiratory complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77842.