Discovery of Linvencorvir (RG7907), a Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein Allosteric Modulator, for the Treatment of Chronic HBV Infection.
Zhang, W., Guo, L., Liu, H., Wu, G., Shi, H., Zhou, M., Zhang, Z., Kou, B., Hu, T., Zhou, Z., Xu, Z., Zhou, X., Zhou, Y., Tian, X., Yang, G., Young, J.A.T., Qiu, H., Ottaviani, G., Xie, J., Mayweg, A.V., Shen, H.C., Zhu, W.(2023) J Med Chem 66: 4253-4270
- PubMed: 36896968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00173
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8I71 - PubMed Abstract:
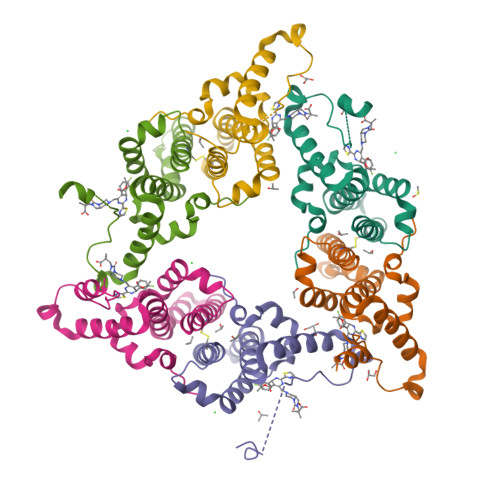
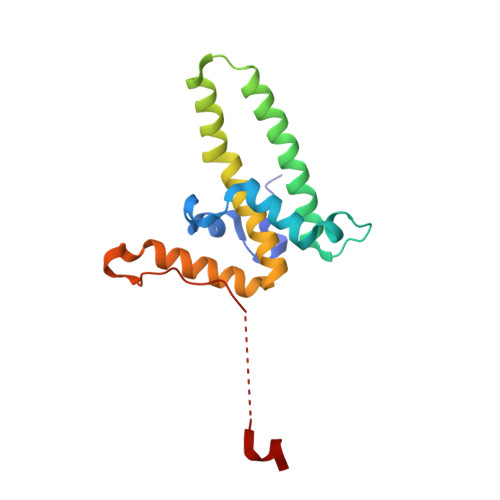
Described herein is the first-time disclosure of Linvencorvir (RG7907), a clinical compound and a hepatitis B virus (HBV) core protein allosteric modulator, for the treatment of chronic HBV infection. Built upon the core structure of hetero aryl dihydropyrimidine, RG7907 was rationally designed by combining all the drug-like features of low CYP3A4 induction, potent anti-HBV activity, high metabolic stability, low hERG liability, and favorable animal pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles. In particular, the chemistry strategy to mitigate CYP3A4 induction through introducing a large, rigid, and polar substituent at the position that has less interaction with the therapeutic biological target (HBV core proteins herein) is of general interest to the medicinal chemistry community. RG7907 demonstrated favorable animal PK, pharmacodynamics, and safety profiles with sufficient safety margins supporting its clinical development in healthy volunteers and HBV-infected patients.
Organizational Affiliation:
China Innovation Center of Roche, Medicinal Chemistry, Building 5, 371 Lishizhen Road, Shanghai 201203, China.