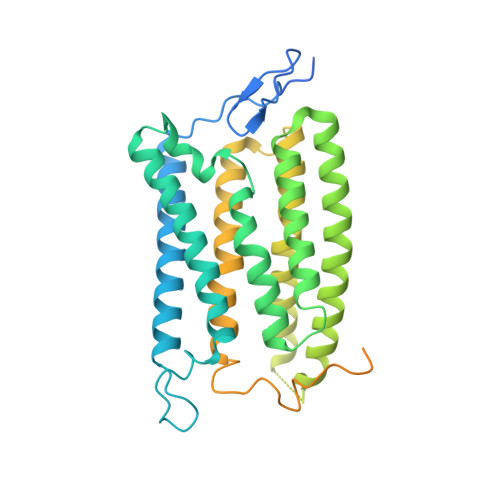
The high-light-sensitivity mechanism and optogenetic properties of the bacteriorhodopsin-like channelrhodopsin GtCCR4.
Tanaka, T., Hososhima, S., Yamashita, Y., Sugimoto, T., Nakamura, T., Shigemura, S., Iida, W., Sano, F.K., Oda, K., Uchihashi, T., Katayama, K., Furutani, Y., Tsunoda, S.P., Shihoya, W., Kandori, H., Nureki, O.(2024) Mol Cell 84: 3530-3544.e6
- PubMed: 39232582
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YEJ, 8YEK, 8YEL - PubMed Abstract:
Channelrhodopsins are microbial light-gated ion channels that can control the firing of neurons in response to light. Among several cation channelrhodopsins identified in Guillardia theta (GtCCRs), GtCCR4 has higher light sensitivity than typical channelrhodopsins. Furthermore, GtCCR4 shows superior properties as an optogenetic tool, such as minimal desensitization. Our structural analyses of GtCCR2 and GtCCR4 revealed that GtCCR4 has an outwardly bent transmembrane helix, resembling the conformation of activated G-protein-coupled receptors. Spectroscopic and electrophysiological comparisons suggested that this helix bend in GtCCR4 omits channel recovery time and contributes to high light sensitivity. An electrophysiological comparison of GtCCR4 and the well-characterized optogenetic tool ChRmine demonstrated that GtCCR4 has superior current continuity and action-potential spike generation with less invasiveness in neurons. We also identified highly active mutants of GtCCR4. These results shed light on the diverse structures and dynamics of microbial rhodopsins and demonstrate the strong optogenetic potential of GtCCR4.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan.